Getting started with Contentful and Symfony
This Symfony CMS tutorial will show you how to setup the ContentfulBundle in your Symfony application and how to access you content inside the framework.
Requirements
The ContentfulBundle requires Symfony 3.4 or 4.0 (and higher), and PHP 7.0.
Install using Symfony Flex
This bundle is compatible with Symfony Flex. In order to use it, please enable contrib recipes by executing this command in your project root:
composer config extra.symfony.allow-contrib trueNow require the actual package:
composer require contentful/contentful-bundleAfter the package is installed, Symfony Flex will do the following:
- Copy the default bundle configuration to
config/packages/contentful.yaml. - Add placeholder environment variables to your
.envfile. - Register the bundle in
config/bundles.php.
Install without Symfony Flex
If you're using this bundle with a pre-Flex install of the Symfony framework, follow these steps. First, require the package:
composer require contentful/contentful-bundleNext you need to enable the Bundle by adding it to your app's kernel in app/AppKernel.php:
public function registerBundles()
{
return [
// ...
new Contentful\ContentfulBundle\ContentfulBundle(),
// ...
];
}Finally, add the bundle configuration to your app/config/config.yml file:
contentful:
delivery:
main:
space: cfexampleapi
token: b4c0n73n7fu1Using the client
Regardless of your method of installing the bundle, you now have a Contentful client registered as a service. The recommended approach is to use dependency injection and type hint the proper interface to access the client. A small controller displaying an entry based on an ID in the URL could look like this:
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Route;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\Exception\NotFoundHttpException;
use Contentful\Core\Exception\NotFoundException;
use Contentful\Delivery\Client\ClientInterface;
class ContentfulController extends Controller
{
/**
* @Route("/entry/{id}")
*/
public function entryAction(string $id, ClientInterface $client)
{
try {
$entry = $client->getEntry($id);
} catch (NotFoundException $contentfulException) {
throw new NotFoundHttpException();
}
return $this->render('default/entry.html.twig', [
'entry' => $entry
]);
}
}To discover how to use the Contentful client, check out the getting started with Contentful and PHP tutorial.
Using the Web Debug Toolbar
The ContentfulBundle integrates with Symfony's Web Debug Toolbar. If the toolbar is shown and there were requests to the Contentful API, there will be a section showing how many requests haven been made against the API.

Clicking on that section will open the Contentful panel in the web profiler.
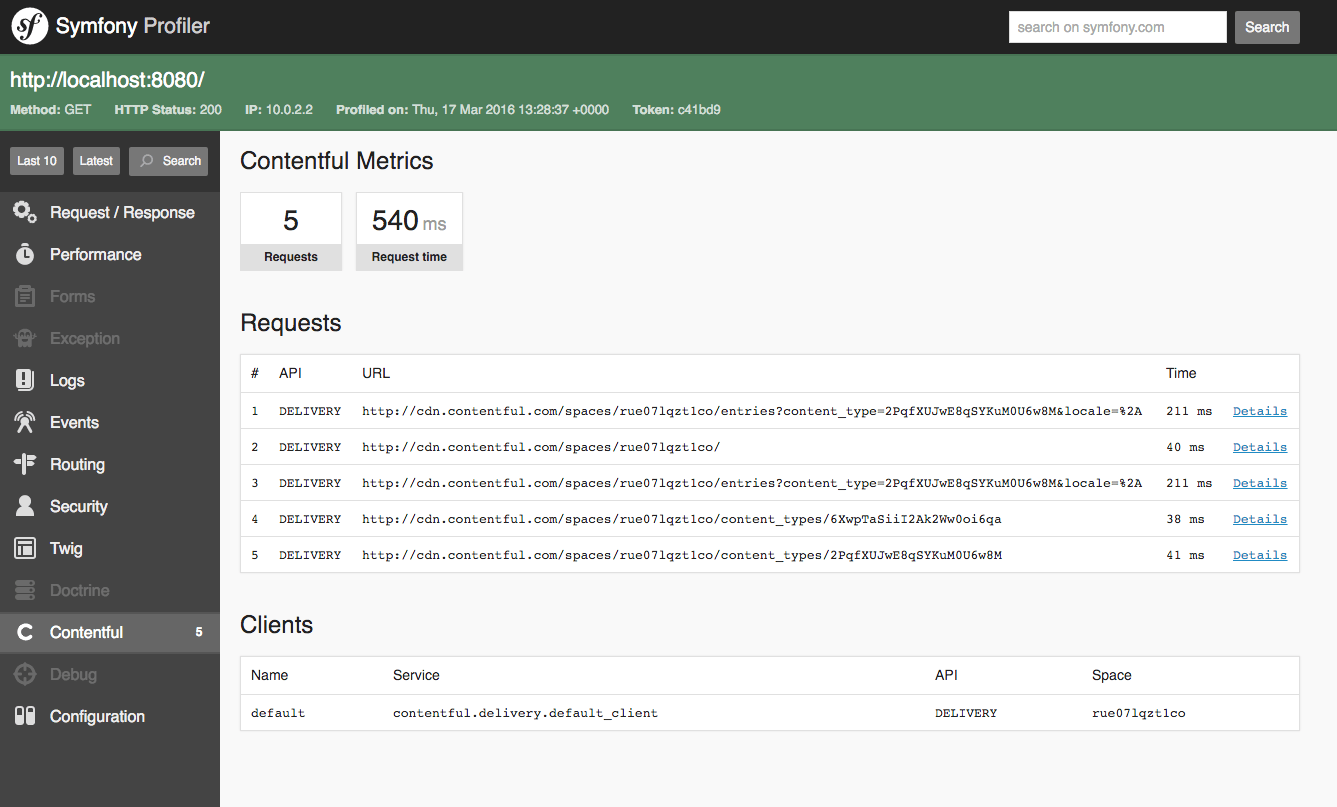
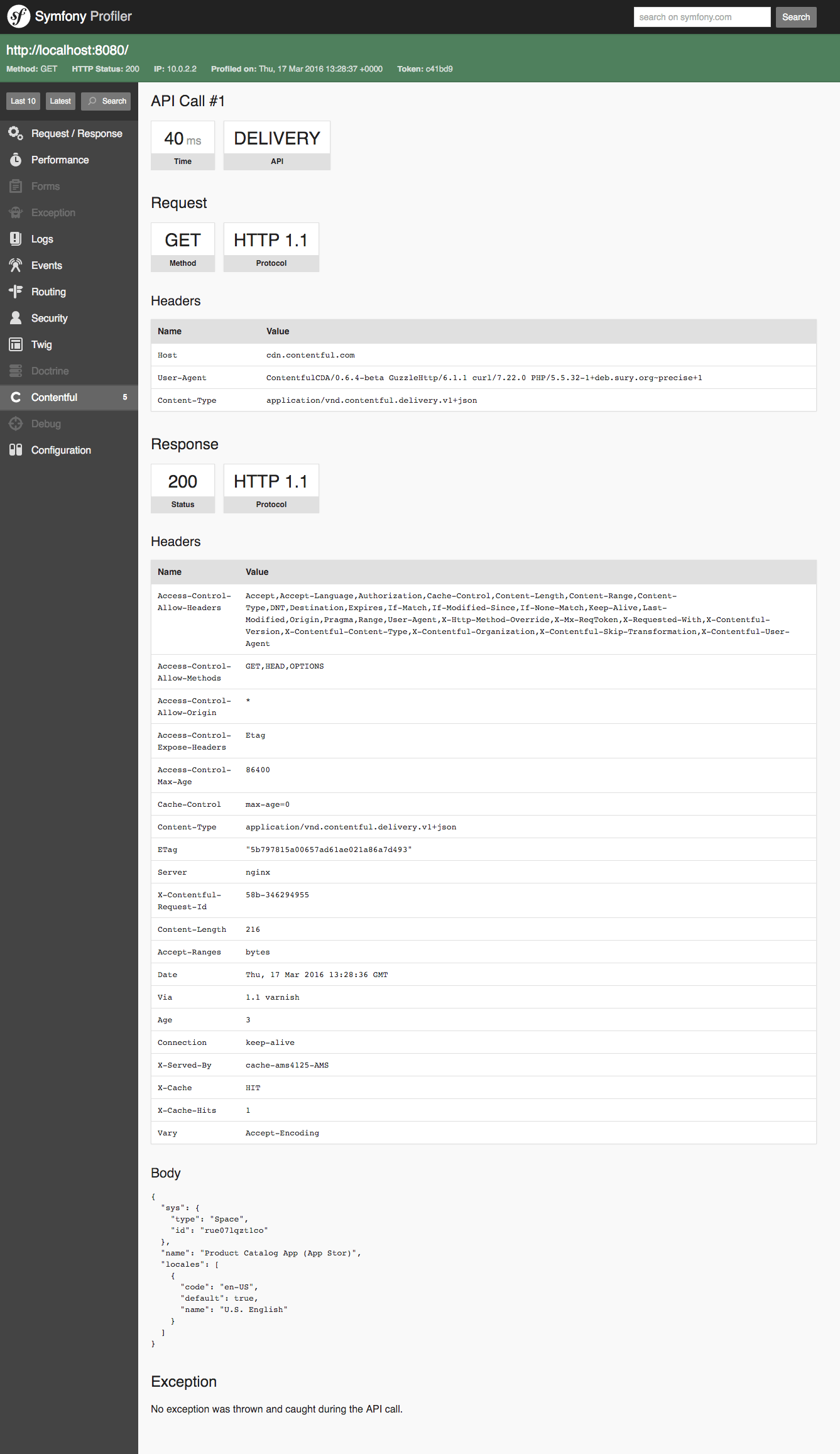
This view shows you a all requests that were made against one of Contentful's API including how long they took. Clicking on the the "Details" in the last column gives you an overview of the request and response and exceptions thrown by the PHP client library.
Configuration options
This bundle supports a variety of configuration options. Regarless of whether your confiuration lives in config/packages/contentful.yaml or app/config/config.yml, here is the full config:
contentful:
delivery:
main:
space: cfexampleapi
token: b4c0n73n7fu1
# Defaults to "master"
environment: master
# The name of the API to use, either "delivery" (default value) or "preview"
api: delivery
options:
# If set, it will be used as the locale on all API calls
locale: en-US
# A URL of a host to use instead of cdn.contentful.com (useful with proxies)
host: https://cdn.contentful.com
# A PSR-3 logger implementation, will default to the system logger
logger: app.logger
# A Guzzle client instance
client: null
cache:
# A PSR-6 cache item pool implementation, will default to the system cache
pool: app.cache
# If true, content type and locale data will be cached during runtime and not on warmup
runtime: true
# If true, entry and asset data will be cached during runtime
content: trueThe bundle also supports a multi-client configuration mode. The options available for every client are the same as above, but you need to mark one of the clients as the default one:
contentful:
delivery:
main:
default: true
space: cfexampleapi
token: b4c0n73n7fu1
preview:
space: cfexampleapi
token: b4c0n73n7fu1
api: previewTo confirm that everything is configured as you wish, execute php bin/console contentful:info in your shell. The output
should look like this:
Contentful clients
==================
--------- ------------------------------------ ---------- -------------- ------------- -----------
Name Service API Space Environment Cache
--------- ------------------------------------ ---------- -------------- ------------- -----------
default contentful.delivery.default_client DELIVERY cfexampleapi master cache.app
--------- ------------------------------------ ---------- -------------- ------------- -----------Conclusion
Now you should be familiar with the basics of how to use Contentful in a Symfony application. You can find the Bundle on GitHub and Packagist. To get a deeper understanding, read some of our other PHP tutorials. If you find a bug, or have an idea how to further integrate with Symfony, please open an issue on GitHub.
