App Actions
Overview
App Action is an entity that allows communication between apps. An app can expose actions that the other apps can call to trigger specific behaviors. App Actions can also be triggered manually by a user.
App Actions are asynchronous and don't return a payload. One could think about an App Action as an asynchronous function that doesn't return a value. As such, App Actions can take arguments and they are defined by means of the parametersSchema property.
With structured App Action results, an App Action Call can now expose a structured outcome on the call resource itself:
- A
statusfield indicates whether the call isprocessing,succeeded, orfailed. - When
statusissucceeded, aresultproperty contains the structured data returned by the action. - When
statusisfailed, anerrorobject describes the failure (id/message and optional details).
You can interact with structured App Action results using the Contentful Management SDK. See the examples in the SDK section ("Using the contentful-management library") for how to invoke and retrieve results using createWithResult, how to fetch a structured call by id using get, and how to retrieve the raw response using getResponse.
Both createWithResult and createWithResponse support optional retry controls in the SDK. You can pass retries and retryInterval to tune how the client polls for completion; otherwise sensible defaults apply.
Here are some examples of how you can use App Actions:
- Sending notifications, e.g. emails, chat messages, SMSes.
- In your CI/CD pipeline, e.g. triggering website builds.
Create an App Action
App Action can be created while editing the app definition for a particular app as seen in the screenshot below:
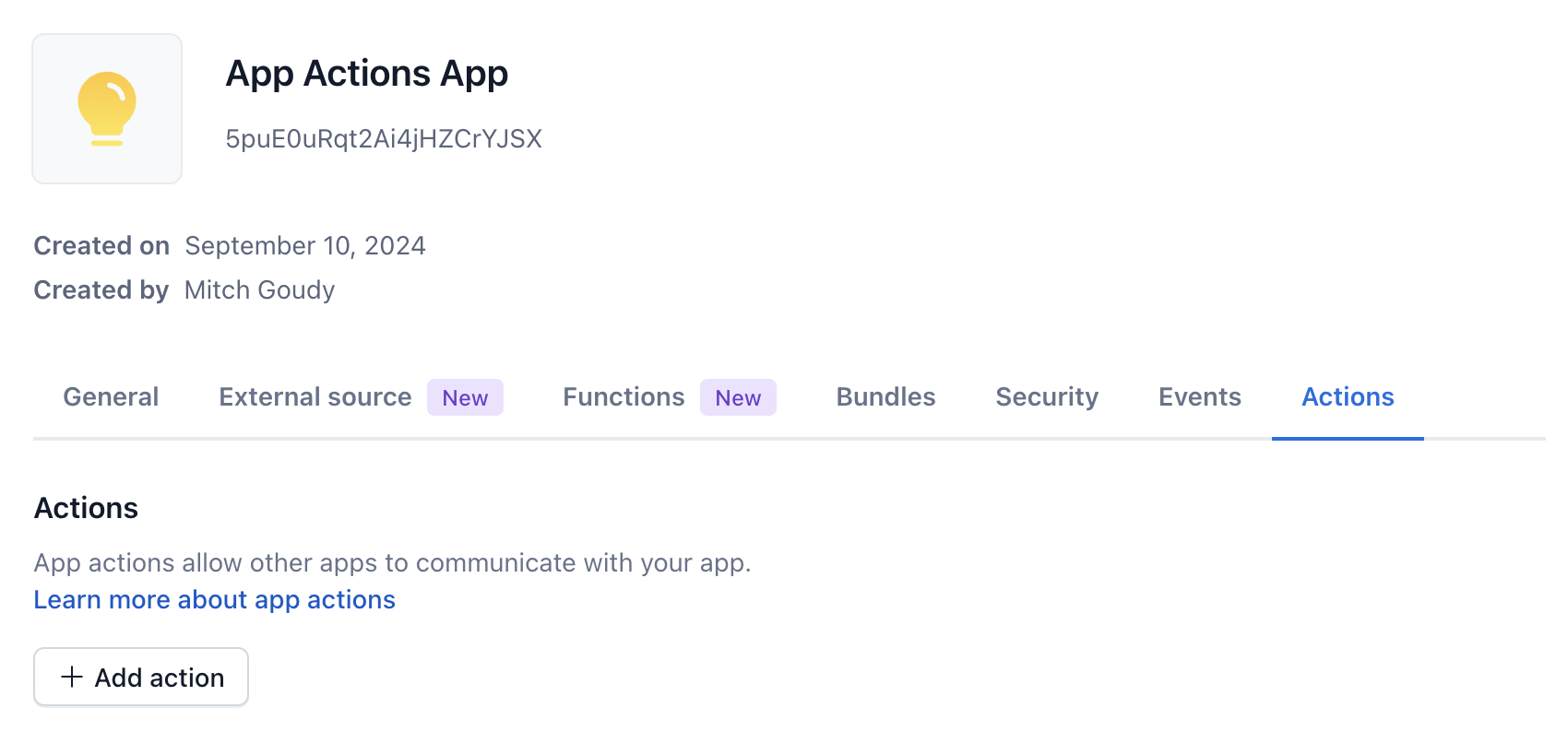
Log in to the Contentful web app.
In the top pane, click Apps and select Manage apps.
Select Your Custom apps.
Go to the required app and under the actions menu select Edit app definition.
Click Add action. A "Create action" window is displayed.
Enter a custom name for your App Action in the Action name field.
In the Action type field, select either Endpoint or Function Invocation:
Endpoint: Provide an Action URL to specify where requests should be sent when the App Action is triggered. The URL must be public and secured with HTTPS.
Function Invocation: Choose a previously uploaded Function that accepts the
appaction.callinvocation type. For more details on creating and managing functions, refer to the Function documentation.
Under the Schema area, optionally define schemas to represent the expected input and output of your App Action:
parametersSchema(JSONSchema4, optional): JSON Schema describing the request payload shape. Contentful validates action parameters against this schema when initiating the call.resultSchema(JSONSchema4, optional): JSON Schema describing the successful result shape. Contentful validates the action result against this schema when processing the call response.
- Click Save action. Your action is saved.
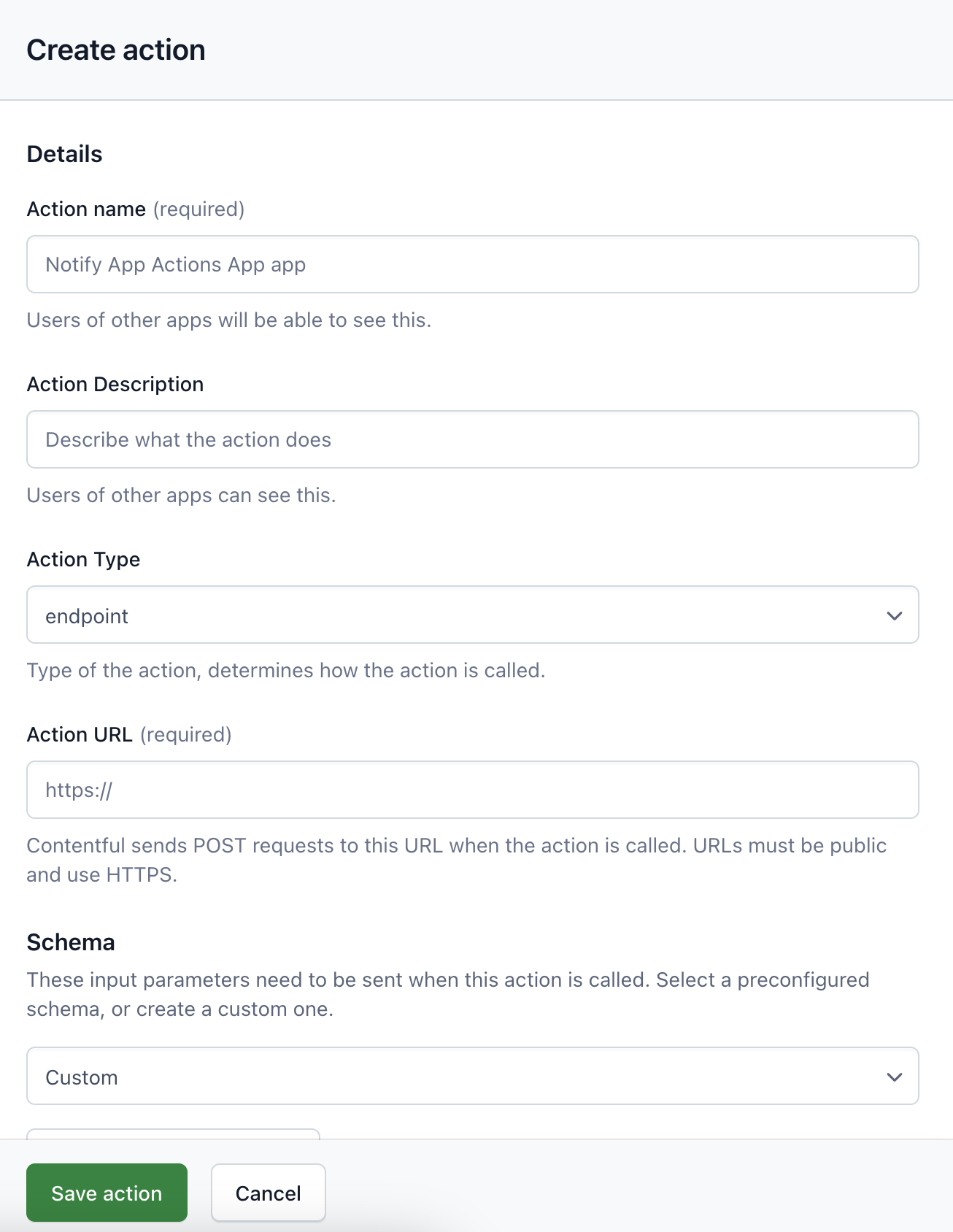
App Action schemas
You can define request and result schemas for custom App Actions. Use parametersSchema to validate the request payload, and resultSchema to validate a successful structured result. See the creation steps above for where to set these in the UI, and the CMA reference for API details.
App Actions calls
To call an action on your app, a consumer app needs to query the CMA. Contentful will then send a signed request to your application. This comes with a few features out of the box:
App Actions are secured by request verification, meaning that your app can check the integrity of every request and only accept calls coming from Apps in Contentful.
App Action parameters are pre-validated (with a provided schema) by Contentful, meaning that you don't need to implement payload validation, once the request is verified.
App Actions are subject to the same rate limiting as the other CMA endpoints, meaning that you won't need to implement rate limiting, if you're happy with the limits CMA runs upon.
App Actions can be triggered only if both
ActionConsumerandActionProviderapps are installed in the same environment, meaning that only authorized apps can act on your data.
Notes
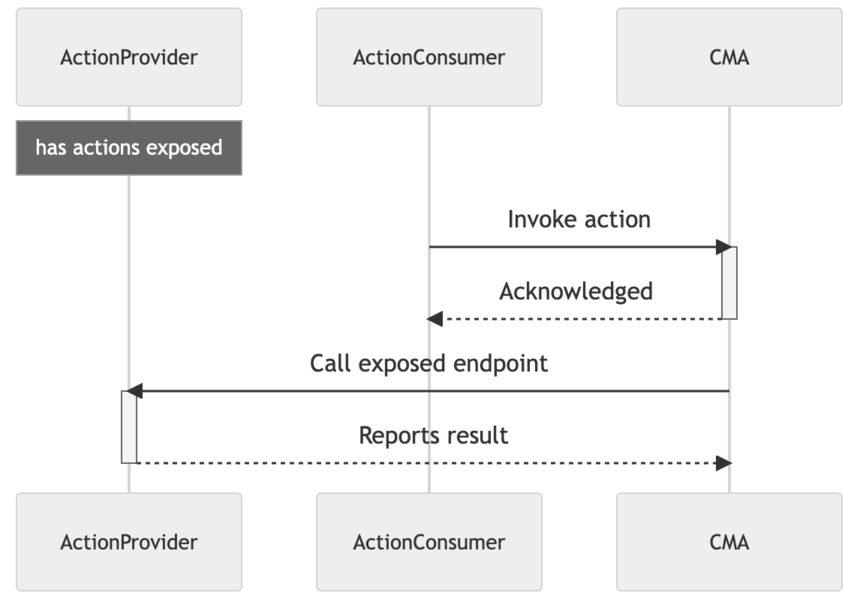
ActionConsumeris a backend app that triggers behaviours in other apps.ActionProvideris a backend app that exposes actions that other apps can trigger.
The diagram below displays an interaction between ActionProvider, ActionConsumer and CMA when an App Action is called.
An example implementation of triggering an AppAction from another app's backend:
import createApp from 'imaginary-http-framework';
import { verifyRequest } from "@contentful/node-apps-toolkit";
import { sendNotification } from './service/imaginary';
import { signingSecret } from './secure-storage';
const app = createApp();
app.post('/send_notification', async (req, res, next) => {
const canonicalRequest = {
method: req.method,
path. req.url,
headers: req.headers,
body: req.body,
}
if (!verifyRequest(signingSecret, canonicalRequest)) {
next(new Error('Forbidden'))
}
const response = await sendNotification(req.body);
res.send(200)
})
app.listen(3000)For a more detailed demonstration, check out our examples.
Call an App Action
After your app action is created, you can call, or invoke the app action by calling the CMA.
To call, or invoke the function, make a request to the Contentful CMA.
To read outcomes for a specific call:
- Get the structured call (status/result/error):
GET /spaces/{spaceId}/environments/{environmentId}/app_installations/{appDefinitionId}/actions/{appActionId}/calls/{callId} - Get the raw executor response (headers/body):
GET /spaces/{spaceId}/environments/{environmentId}/app_installations/{appDefinitionId}/actions/{appActionId}/calls/{callId}/response
To view explanations for common app actions calls errors, check Contentful CMA reference.
App Action categories
Common use cases would require you to rewrite the same App Action over and over. With App Action categories you can simply reference one of the pre-defined schemas, without having to redefine the same parameters multiple times.
Let's assume your app needs to perform an operation and needs to trigger a notification to different services. Utilising categories, you can simply call App Actions whose category is Notification and ultimately integrate with all of them at once: you will only rely on the Notification and you are good to go.
Additionally, App Actions with some specific App Action Categories will show up in specific locations of the user interface.
App Action Categories are versioned in a semantic way: the first digit indicates a breaking change and the second digit all the other changes.
To view the list and get all App Actions categories, check Contentful CMA reference.
